Balance Growth Strategic Development Paradigm
"From Poverty and Human Suffering to Sustainability & Prosperity©"
The Process of Using the Vehicle of Enterprise Development Through The Balance Growth Paradigm to Mitigate & Alleviate Poverty as Measured by the Indices of Sustainability and Prosperity©
By Samual W. Scott, Ph.D., Spring 2001
USDOE Project - APEC Energy for Sustainable Development
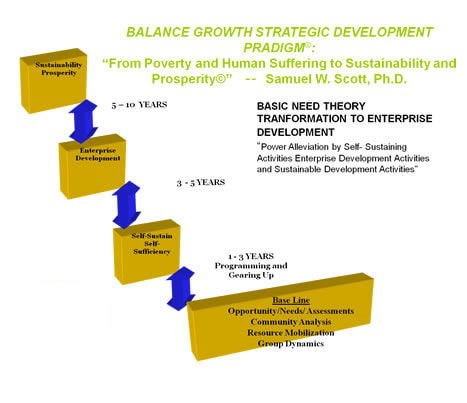
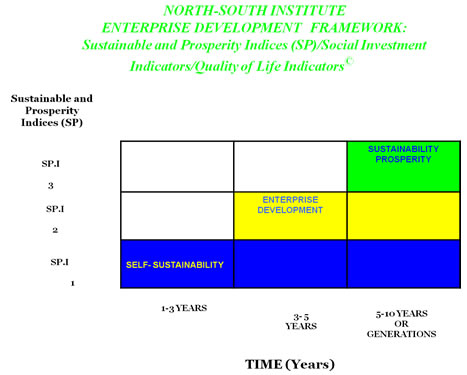
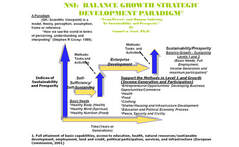
NSI's Balance Growth Paradigm definition is based on Multi-discipline Holistic Approach that fundamentally consists of sequential steps which focus on mitigating poverty as well as human suffering that ultimately lead towards prosperity in healthy, education, food,, clothing, shelter housing, employment, business development opportunities (commerce), civility, peace and security, community sponsored services and infrastructure. The model starts out from the basic needs theory addressing the need for food, clothing, shelter, education, healthcare. This is where household entity attains that level, then certain surpluses are generated. The need now exist for organized transactions, and markets where the outputs will be marketed and consume outside of that unit.
Once this level is attained the model is transformed from basic needs/self sufficiency/self sustaining mode to enterprise development/entrepreneurship resulting in increased incomes to the unit. This is defined as Level II. The next level is that of sustaining the former levels, this is where the entity continues to be organized and implement financial and non-financial structures and systems to sustain earnings for personal family household welfare and satisfying the existing markets. This defined as Level III. This phase is called the Sustainable Prosperity stage. For organized communities this can take as short as 7-10 years to as longs as a few generations, given that development is not linear, and there will be overlapping phase of different individuals and family units within a community, Graphic representation of the paradigm is shown in the following figures.
The Process of Using the Vehicle of Enterprise Development Through The Balance Growth Paradigm to Mitigate & Alleviate Poverty as Measured by the Indices of Sustainability and Prosperity©
By Samual W. Scott, Ph.D., Spring 2001
USDOE Project - APEC Energy for Sustainable Development
NSI's Balance Growth Paradigm definition is based on Multi-discipline Holistic Approach that fundamentally consists of sequential steps which focus on mitigating poverty as well as human suffering that ultimately lead towards prosperity in healthy, education, food,, clothing, shelter housing, employment, business development opportunities (commerce), civility, peace and security, community sponsored services and infrastructure. The model starts out from the basic needs theory addressing the need for food, clothing, shelter, education, healthcare. This is where household entity attains that level, then certain surpluses are generated. The need now exist for organized transactions, and markets where the outputs will be marketed and consume outside of that unit.
Once this level is attained the model is transformed from basic needs/self sufficiency/self sustaining mode to enterprise development/entrepreneurship resulting in increased incomes to the unit. This is defined as Level II. The next level is that of sustaining the former levels, this is where the entity continues to be organized and implement financial and non-financial structures and systems to sustain earnings for personal family household welfare and satisfying the existing markets. This defined as Level III. This phase is called the Sustainable Prosperity stage. For organized communities this can take as short as 7-10 years to as longs as a few generations, given that development is not linear, and there will be overlapping phase of different individuals and family units within a community, Graphic representation of the paradigm is shown in the following figures.
Enterprise Development Definitions
Definition # 1. “Enterprise Development is the process of increasing the capacity of individuals, families, groups and organizations to supply useful goods and services profitably to the market. It supports the development of essential business skills, enabling individuals to adapt to changing market conditions, and maintain business growth. Support may be directed at improving services for entrepreneurs, such as savings and credit; management training; marketing linkages; and technology transfer - or improving the policy, regulatory or operating environment that enables business to thrive” (2000 DFID ).
Definition # 2. Sustainable (Values-based) Enterprise Development (SED) is the process of sequential steps within a Balance Growth Strategic framework resulting in increasing the capacity of individuals, families, groups and organizations to supply useful goods and services profitably to the market within limits set by ecology and social values (Scott and Colley, September 2007). Taking into consideration viabilities at the technical, economic, social and environmental levels, SED supports:
Definition # 1. “Enterprise Development is the process of increasing the capacity of individuals, families, groups and organizations to supply useful goods and services profitably to the market. It supports the development of essential business skills, enabling individuals to adapt to changing market conditions, and maintain business growth. Support may be directed at improving services for entrepreneurs, such as savings and credit; management training; marketing linkages; and technology transfer - or improving the policy, regulatory or operating environment that enables business to thrive” (2000 DFID ).
Definition # 2. Sustainable (Values-based) Enterprise Development (SED) is the process of sequential steps within a Balance Growth Strategic framework resulting in increasing the capacity of individuals, families, groups and organizations to supply useful goods and services profitably to the market within limits set by ecology and social values (Scott and Colley, September 2007). Taking into consideration viabilities at the technical, economic, social and environmental levels, SED supports:
- Development of essentials skills
- Enabling individuals to adapt to changing market conditions
- Maintaining business growth
- Improving the services for entrepreneurs such as savings, credit, management training, market linkages, and technology transfer
- Improving the policy , regulatory and operating environment that enable business to thrive
- Establishing sound procedures that result in the utilization of resources without extreme harm to the environment within the local context:
- Sustainable harvest/extraction such that the environment can regenerate itself
- Ensuring biodiversity and species
- Recycling of natural waste from production and processing
- Conservation of soil, water and the air
- Enabling people to make livelihoods from agro-ecological opportunities, such as eco-tourism, permaculture and organic farming
- Promotion of production and use of renewable resources